Some say that nothing is impossible. It is true that there were cases that someone claimed differently, however in this case we say that everything is possible. Well, can you make a suspension that is both partially dependent and independent at the same time? It turns out yes! Let’s look at the suspension work of the beam with torsion bars.
The torsion beam is a very interesting technical solution. When one wheel encounters an unevenness on the road that is not too large, suspension work only occurs on one side. We can simplify that the suspension behaves independently in that matter. When the unevenness is greater, then the wheel on the opposite side also reacts – as in a dependent suspension. This is because the transverse axle is in front of the wheels and allows a certain range of work through the torsion bars. Thanks to this, it maintains the above characteristic, and the torsion bars also acts as a anti-roll bar, although in some cases the anti-roll bar is still used as an additional element.
Torsion bars used in the construction perform the function of a coil or leaf springs. One of the bars also replaces the anti-roll bar. The use of the above elements means that we are dealing with semi-dependent suspension. As described earlier, the movement of one wheel has a limited effect on the work of the other wheel on the same axle.
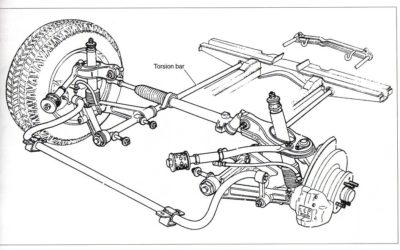
Interestingly, the torsion bars were also used for the front axle in the past. They still performed the same function – i.e. the role of a coil spring or a leaf spring. In this case, they were placed longitudinally, which is completely different comparing to the rear axle application. This solution was used in the Alfa Romeo Alfetta. The diagram of the front suspension of this vehicle is presented below. This suspension was also used in other vehicles. Among other cars, several Chrysler models were equipped with such front suspension system. An interesting advantage of this solution is the fact that the suspension was completely independent.
Why do we use a torsion bar beam?

The indisputable advantage of using this type of suspension are the compact dimensions. Thanks to the solution design, the car can have a flat trunk, which significantly improves ergonomics. Despite not so complicated construction (or at least compared to the multi-link system), the solution provides good driving characteristics and high comfort. Most often, the beam with torsion bars is found in Peugeot and Renault vehicles. Interestingly, this solution had its premiere in German production cars. The Audi 50, Volkswagen Golf, Scirocco and Polo were the first vehicles to use a torsion bar beam. It all started in the 1970s.
Does the solution have any cons?
Unfortunately, the torsion bar beam is not the most durable solution when it comes to the rear suspension. Remember that it works under a heavy load, and during it is subjected to considerable forces in various directions. The suspension comes into contact with extremely adverse conditions, such as snow and rain, dirt or accumulating moisture. These factors damage the seals, which has a negative effect on the needle bearings inside. This is the most common cause of torsion bar beam failure. If the failure is not discovered quickly enough, the swingarm mounting pin is damaged and the beam must be regenerated.
Side impact are another common cause of the damage. The torsion bar beam is very vulnerable at impacts to the side of the wheel. Such hit often causes the element to warp and the only recipe for repair is to replace the entire beam. In an event of a strong side impact on the vehicle wheel, the mounting point of the beam in the vehicle chassis can be damaged. In this case, the repair costs may exceed the value of the vehicle.
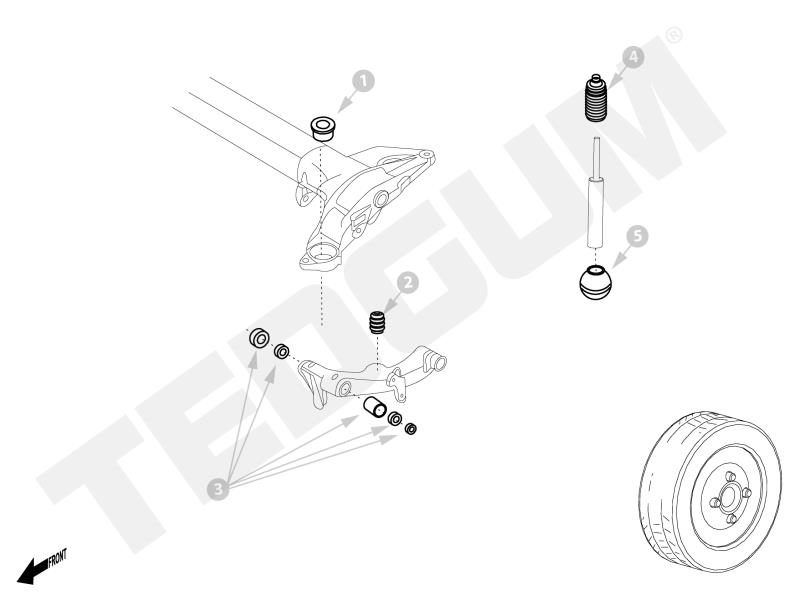
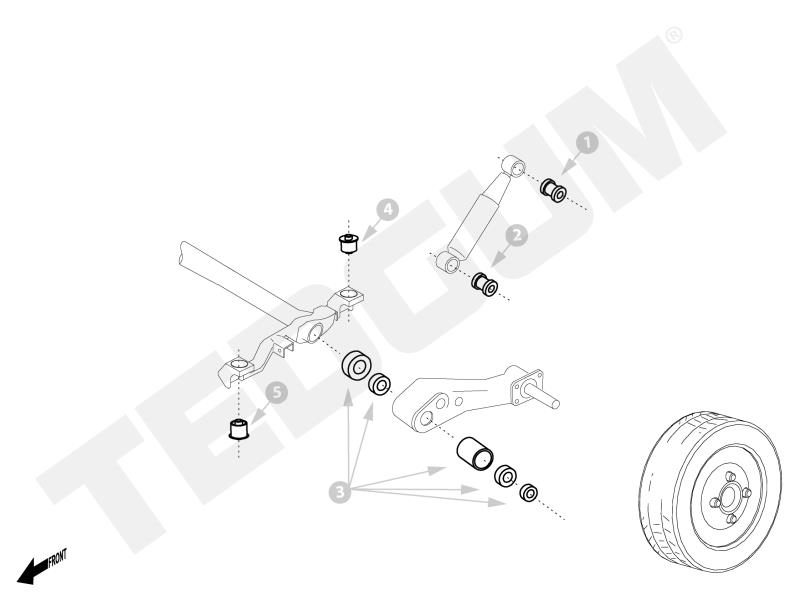
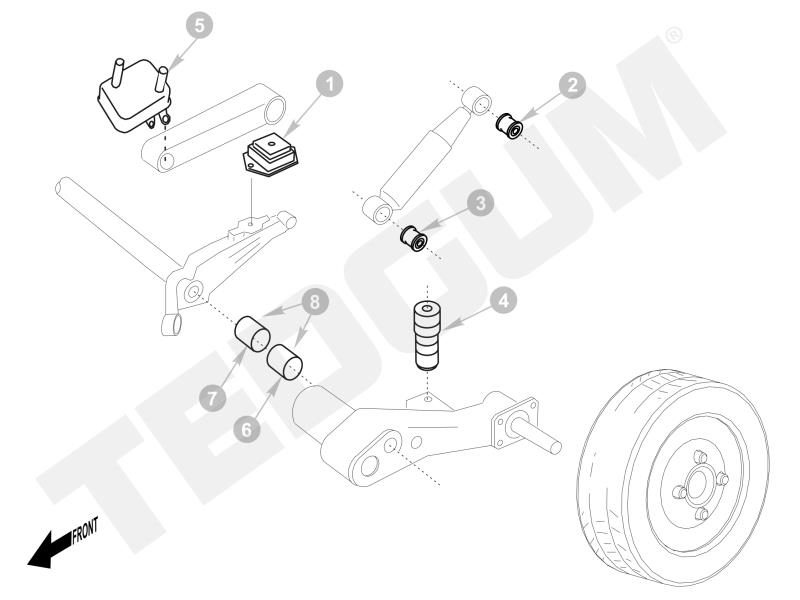
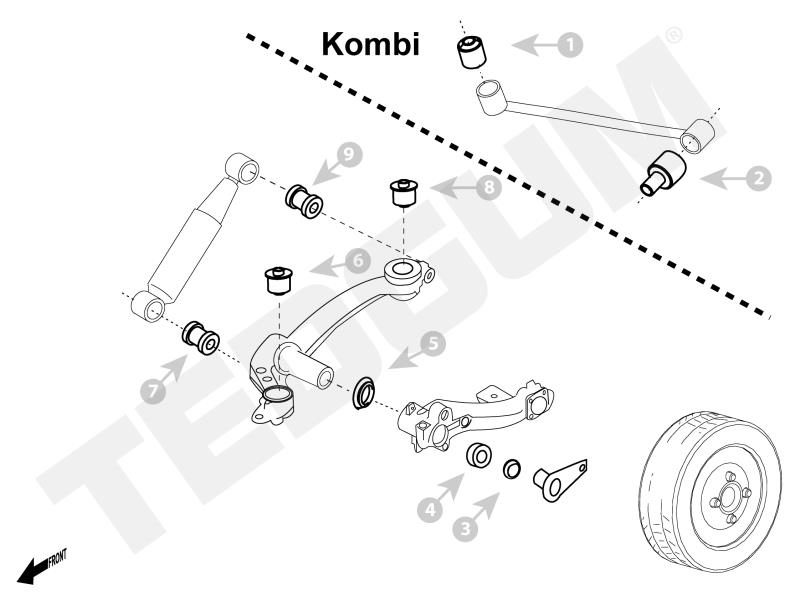
Early diagnosed damage can be repaired at a relatively low cost. The key is to recognize the fault in its initial phase. If the bearing or sealing are the only damaged elements, only those can be replaced which is a lot cheaper than a full torsion beam regeneration. In this case, repair kits come to the rescue. Depending on the type of beam, they can consist of 3, 4 or more elements.
Below are the exemplary repair kits for torsion bars. More can be found in our free online catalogue.
Key tips regarding the service of a car equipped with a torsion bar beam
Just as with many other components, it is not recommended postponing repairs to the last minute. Postponing all repairs to later usually results in a larger bill at the car workshop. It is not always necessary to replace the entire beam or to regenerate it. The beam with torsion bars is not a particularly frequent-failing solution, but it is worth checking its condition regularly.
The key is to quickly diagnose the fault. Therefore, any disturbing sounds coming from the rear suspension of the vehicle cannot be ignored. Moreover, it is also good practice to regularly visually check the condition of the beam seals. Thanks to this, it is possible to identify a fault in its initial stage, which will significantly reduce the scope of required repairs. Usually, such repair is limited to the replacement of seals and bearings, which results in a much lower cost than the beam regeneration.